prepFAST IC – Total Elemental Analysis & Speciation

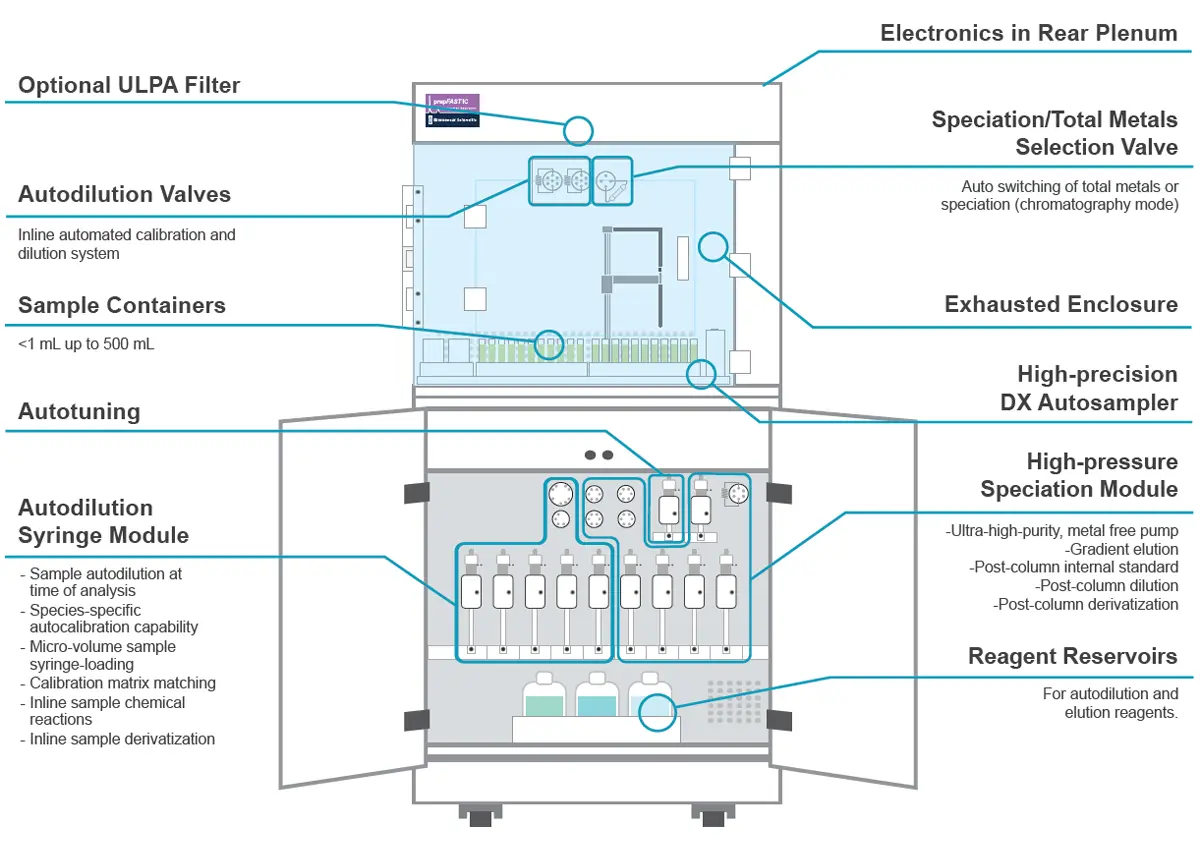
Trace metal laboratories are often required to speciate samples at frequencies that do not require a dedicated LC-ICPMS. As a result, costly LC systems need to be constantly attached and detached from the ICPMS. The prepFAST IC is a single platform capable of providing total elemental analysis and elemental speciation. The user can seamlessly switch between total metal analysis and speciation without having to change any hardware, solutions, or samples. In addition the system can autocalibrate from single stock standards and autodilute samples for both total metal and speciation analysis.
prepFAST IC Features
- FAST uptake, stabilization, & washout
- High Performance P-series valve systems
- Superior DX autosampler
- Completely metal free system
- Autocalibrate total metals & species
- Autodilute total metals & species
- Auto switching between total metal analysis and speciation
- Integrated chromatography
- Gradient elution
- Automated tuning
- Syringe loading for all sample types including viscous

prepFAST IC
List below displays the species that are separated with each method
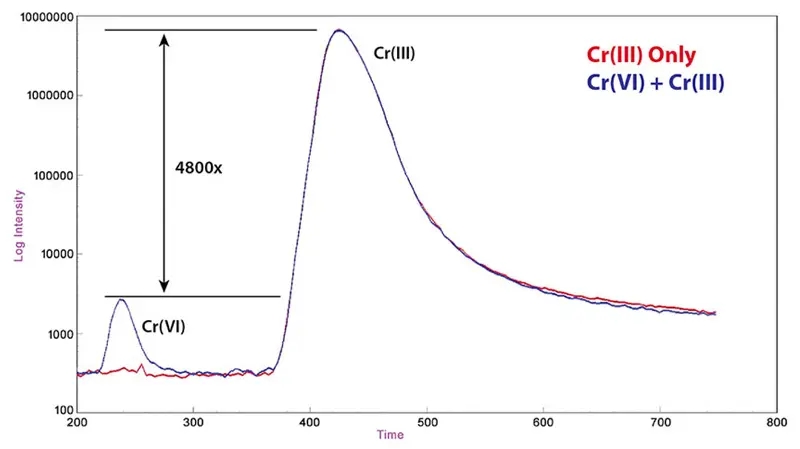
- ICX-Cr36: Cr(VI), Cr (III)
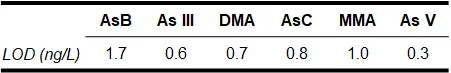
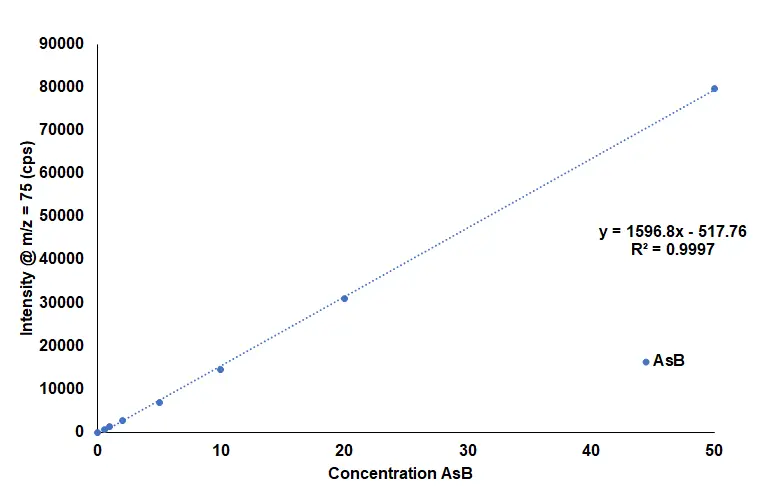
- ICX-As35: AsB, AsC, DMA, MMA, As(III), As(V)
- ICX-AsTMAO: AsB, AsC, DMA, MMA, As(III), As(V), TMAO
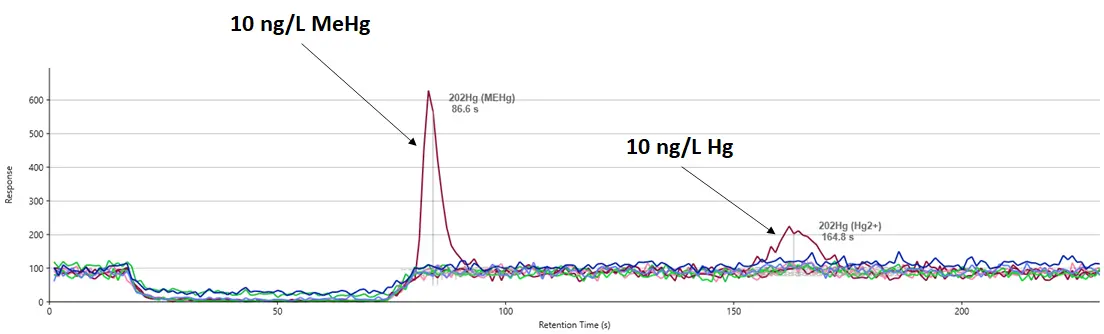
- ICX-Hg: Hg, Me-Hg
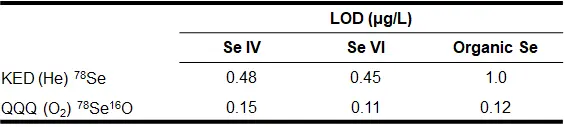
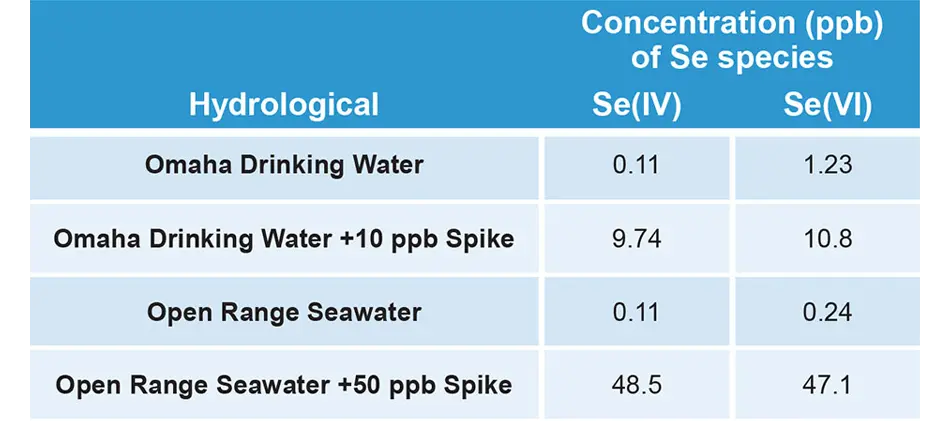
- ICX-Se46: Org-Se, Se(IV), Se(VI)
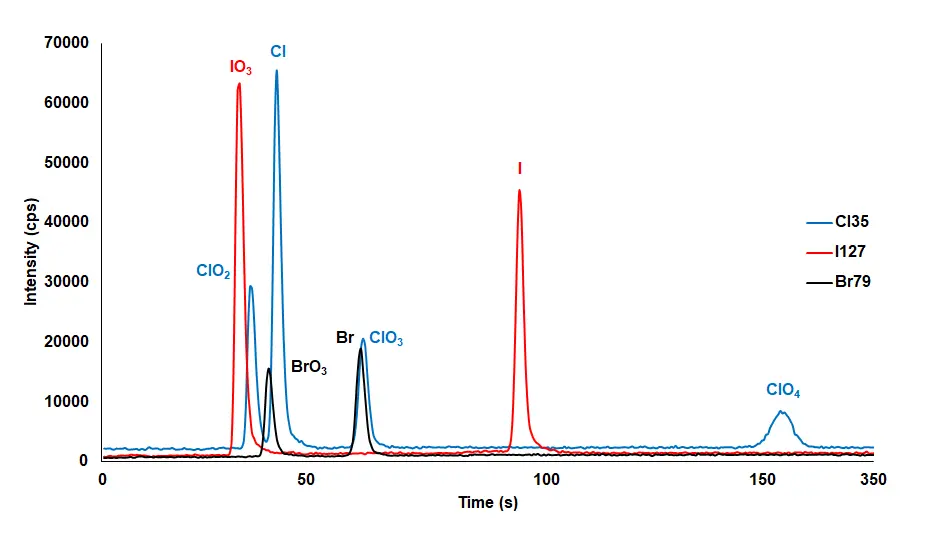
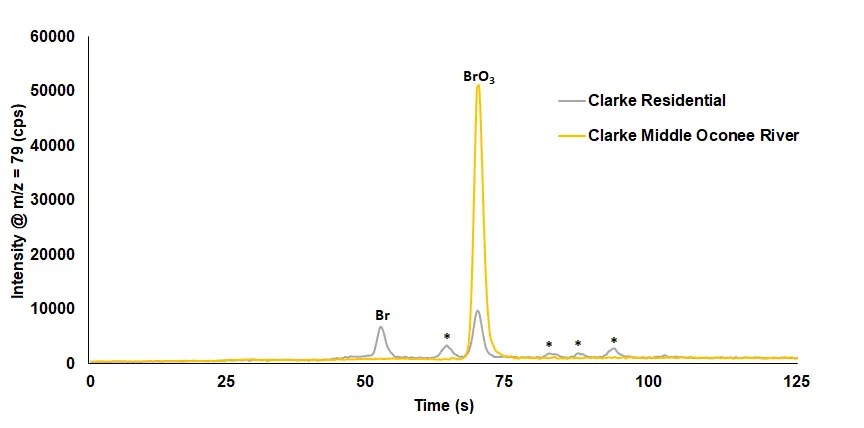
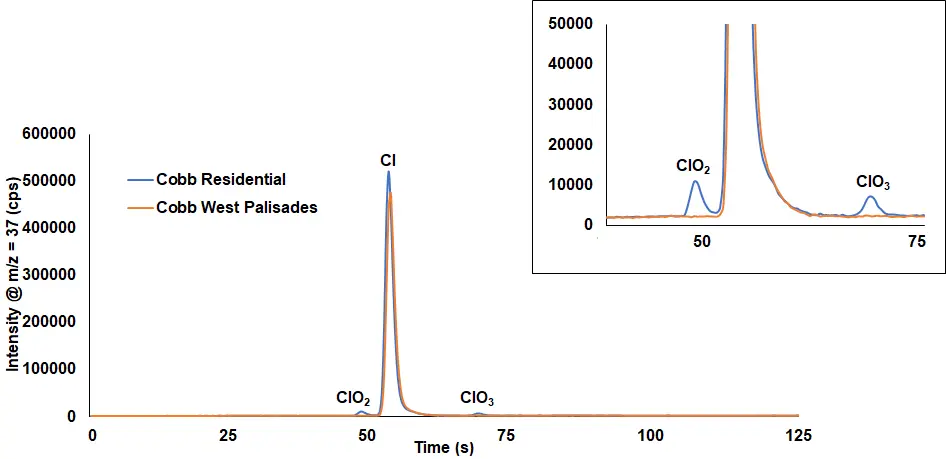
- ICX-ClBrI: Cl, ClO2, ClO3, ClO4, Br, BrO3, I, IO3
- ICX-Gd-50: Gd-based contrast agents
- ICX-Cu: Bound Cu, Free Cu
- ICX-Fe23: Fe(II), Fe(III)
- ICX-V45: V(IV), V(V)
- ICX-PO234: PO2, PO3, PO4
- ICX-UTEVA: U, trace metals